![]()
The adjusting entry for taxes updates the Prepaid Taxes and Taxes Expense Mental Health Billing balances to reflect what you really have at the end of the month. The adjusting entry TRANSFERS $100 from Prepaid Taxes to Taxes Expense. It is journalized and posted BEFORE financial statements are prepared so that the income statement and balance sheet show the correct, up-to-date amounts.
- General expenses pertain to operational overhead expenses that impact the entire business.
- Recording insurance transactions properly is key to accurate financial statements.
- The left side of the T represents the debit side, and the right side represents the credit side.
- This article clarifies when insurance transactions are debited or credited.
- This guide will break down what is debit and credit, explain how they apply to different account types, and provide debit and credit examples to help you understand them.
Example of Payment for Insurance Expense
- It also sets up automatic monthly adjusting entries to debit Insurance Expense for $200 and to credit Prepaid Insurance for $200 on the last day of each month.
- The main advantage of prepaid insurance is that companies occasionally pay bills in advance to gain a discount.
- Insurance expense is a charge a business incurs to protect its operations against adverse commercial or life events.
- The company requires to record unexpired insurance when payment is transferred to the insurance company.
- If the business owner pays for their insurance with their own money, then nothing gets entered to the business bookkeeping records.
- As the prepaid insurance expires throughout the passage of time, the company needs to transfer the prepaid insurance that has expired in the period to the insurance expense.
There are two ways this information can be worded, both resulting in the same adjusting entry above. During the month you will use some of this rent, but you will wait until the end of the month to account for what has expired. During the month you will use some of this insurance, but you will wait until the end of the month to account for what has expired.
Example Entries with Debits and Credits for Common Scenarios:
It will increase the insurance expense by $ 10,000 on income statement and reduce prepaid expenses from current assets. Handling insurance expiration and making the necessary adjusting entries is an essential aspect of maintaining accurate financial records. Prepaid insurance represents an asset for a business, reflecting a payment made for coverage that extends into future periods. It is considered an asset because it provides a future economic benefit in the form of services or coverage yet to be received.
How to Calculate the Current Ratio in Accounting
- The initial payment is always debited to prepaid insurance, reflecting the future economic benefit of insurance coverage.
- Once the bill has been paid in full, the accounts payable will be decreased with a debit entry.
- An expense account reflects the cost incurred to generate revenue during an accounting period.
- Insurance accounting involves more than just the recording of premium payments and claim reimbursements.
- Insurance that is paid in advance is considered as a prepaid expense under the current asset in the balance sheet of the company.
- Step 2 – At the time when the expense is transferred to “Profit & Loss A/c”.
For example, rent payments, interest payments, electricity bills, administration expenses, selling expenses, etc. Insurance expense, also known as insurance premium, is the cost one pays to insurance companies to cover their risk from any unexpected catastrophe. It is calculated as a set percentage of the sum insured and is paid at a regular pre-specified period. Insurance expense and insurance payable are distinct terms; one is an expense and the other is a liability. However, both terms interrelate because there wouldn’t be an insurance payable amount without an insurance expense. This is because the debt only emerges if a policyholder does not pay the premiums on time and in accordance with contractual agreements.
- Other operating risks against which an organization can insure its activities include casualty, property, legal liability, credit and life.
- Some insurance payments can go on to the Profit and Loss Report and some must go on the Balance Sheet.
- The company has paid $10,000 of the insurance premium for the entire year at the beginning of the first quarter.
- However, research and development (R&D) costs are not considered administrative expenses.
Prepaid Insurance Journal Entry ACCA Questions

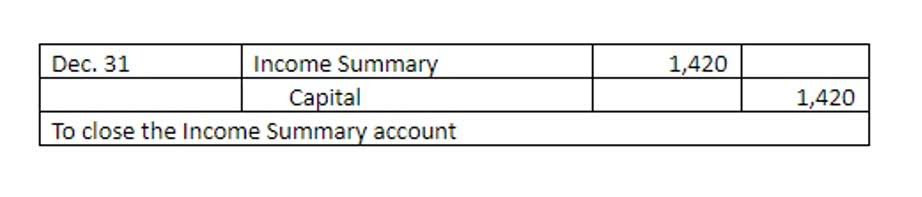
Revenue accounts, reflecting income earned from business activities, increase with a credit and decrease with a debit. Expense accounts, which represent costs incurred to generate revenue, increase with a debit and decrease with a credit, as expenses reduce equity. The adjusting entry for prepaid insurance at the end of each month is a debit for insurance expense and a credit for prepaid insurance, as stated in Example 1, question 3.

Is insurance an income or expense?
Therefore, the Prepaid Insurance asset account receives a debit for the premium paid. Simultaneously, the Cash account receives a credit for the identical amount. For instance, if a business pays $1,200 for a one-year insurance policy, the Prepaid Insurance account would be debited for $1,200, and the Cash account would be credited for $1,200. On July 1, the company receives a premium refund of $120 from the insurance company. The company records the refund with a debit to Cash and a credit to Prepaid Insurance. Prior to issuing the December 31 financial statements, the company must remove the $120 credit payroll balance in Prepaid Insurance by debiting Prepaid Insurance and crediting Insurance Expense.

The recurring monthly adjusting entries are not changed, but a credit balance in Prepaid Insurance must be removed by debiting Prepaid Insurance and crediting Insurance Expense. When payment is made, either in full or with monthly payments, the bill will decrease, which means the accounts payable account will decrease. Businesses must track financial is insurance expense a debit or credit inflows and outflows to understand their financial position.
